The Great Plains of India, point-wise, is explained through a map. Only important material for the competitive exam has been included.
Great Plains of India | Great Plains of North India
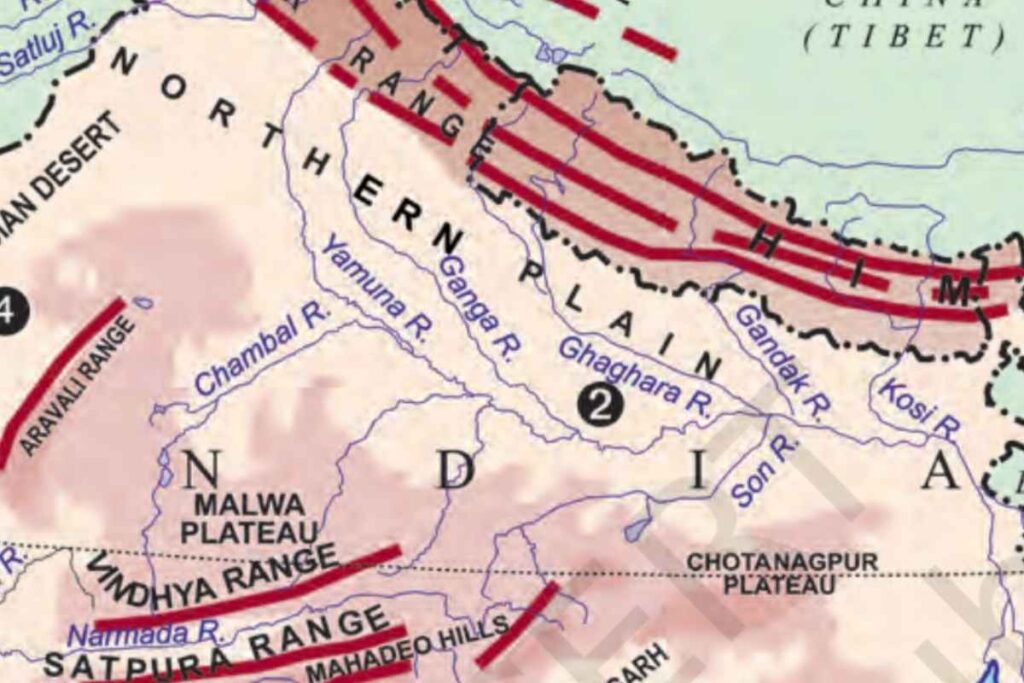
- This is the latest physical region that has been formed after the origin of the Himalayas.
- This vast plain has been formed due to the filling of the trough as a result of alluvial deposits brought by the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra rivers.
- It is spread over an area of 7 lakh square kilometers which is about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km wide. Most of it is in Uttar Pradesh, the remaining part is in the states of Punjab, Haryana, Bihar, West Bengal, and Assam.
- The depth of the deposited alluvium is found to be about 2000 m. The depth of the alluvium is highest near the Himalayas while the depth is less in the adjoining part of the peninsular plateau.
- According to Mr. Sweis, there was a tectonic trough at the place of this plain in the past, which was formed during the formation of the Himalayas.
- It is the world’s most alluvial deposited and fixed plain, its slope is very slow.
- Due to rich soil cover, adequate water availability, and favorable climate, it is a highly productive region of India from the point of view of agriculture, due to which is a densely populated region.
- The rivers flowing here form the world’s largest deltas at their mouths, such as the Sundarbans delta.
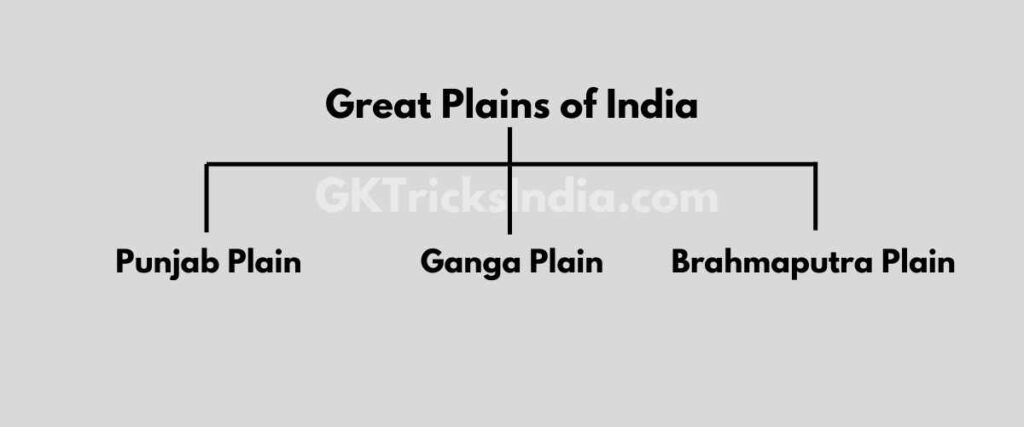
The vast plain of North India can be broadly divided into 3 sections
- Punjab Plain
- Ganga plain
- Brahmaputra plain
Punjab Plain
- The western part of the northern plain
- Formed by the Indus and its tributaries
- Most part in Pakistan
- The number of doabs is very high
Ganga plain
- Widespread in the northern Indian states of Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- It extends between the Ghaggar and Teesta rivers.
Brahmaputra plain
- Especially in Assam
- Presence of river islands and sand barriers
- Majuli Island is the largest island in the world among these islands.
On the basis of morphological variation, the northern plain is divided into four parts.
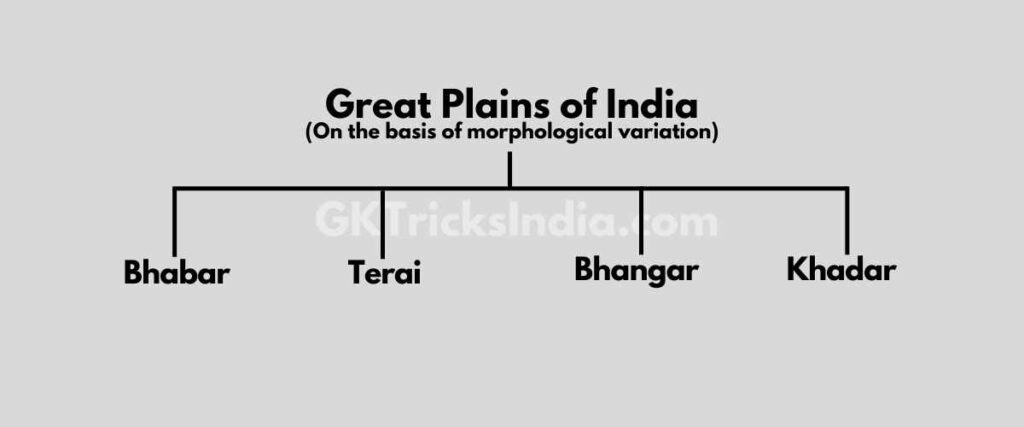
Bhabar
- The rivers, while descending from the mountains, deposit gutika in a wide strip of 8 to 16 km on the slopes of Shivalik.
- All rivers disappear in Bhabar
- This ground can also be called the Alluvial Fan of Shivalik.
Terai
- To the south of Babur, these rivers recede and form a moist and marshy area.
- Due to the moist and marshy area, due to the breeding of mosquitoes, the outbreak of malaria is high in this area.
Bhangar
- The largest part of the northern plain is made up of old alluvium.
- It is situated on top of the flood plains of rivers and exhibits an altar-like shape.
- Extension Punjab Haryana Rajasthan Western Uttar Pradesh.
- Selective deposits in the soil, are called pebbles in the local language.
Khadar
- The new and young deposits of the flood plains are called Khadar.
- These are rebuilt almost annually so it is fertile.
- Expansion Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Assam.
Read also: Mountainous Region of India
Questions and Answers
Which is the largest plains in India?
The northern plain is the largest plain in India. It covers a 7 lakh square km. The plain, which is a heavily inhabited physiographic region, is approximately 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km wide.
How were the great Indian plains formed?
The great plains in India were created by the sedimentary deposits, or alluvium, that the rivers transported from the Himalayas through their erosion. India’s most recent geological block is the plains, which were developed during the Quaternary period of the Pleistocene and Holocene.
What is the importance of Great Plains of India?
These are crucial because of the region’s navigable rivers, flat terrain that is ideal for highways and railroads, and best-in-class irrigational infrastructure.
Which Indian states are plains?
The nation’s capital, New Delhi, as well as the major and politically crucial states of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Bihar are all located in this region. It is a sizable stretch of flat ground created by the Ganges River in the northern regions of contemporary India and the bordering Himalayan mountains.
Describe the Northern Great Plains of India
The interaction of the three main river systems, the Indus, the Ganga, and the Brahmaputra, as well as their tributaries, has created the northern plain. This plain covers 7 lakh square kilometers. The plain, which is a heavily inhabited physiographic region, is approximately 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km wide.
Friends, if you find any kind of mistake or error in this article then please comment or mail us, so that we can rectify these mistakes.

